CONDITIONS
Your initial consultation is FREE and you do not need a
prescription from a doctor.
- Initial Consultations
- Fittings & Adjustments
- Follow Up Visits
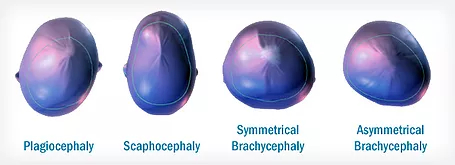
Plagiocephaly
Plagiocephaly is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side) of the skull resulting in an abnormal head shape. If your child’s head is misshapen as a result of the birthing process, this trait may gradually correct itself. However, if an abnormal head shape persists beyond six weeks of age, your infant should be evaluated by a professional. There are several different types and combinations of Plagiocephaly and head shapes.

Plagiocephaly Head Shapes
Plagiocephaly is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side) of the skull resulting in an abnormal head shape. If your child’s head is misshapen as a result of the birthing process, this trait may gradually correct itself. However, if an abnormal head shape persists beyond six weeks of age, your infant should be evaluated by a professional. There are several different types and combinations of Plagiocephaly and head shapes.
Deformational Scaphocephaly is characterized by a long and narrow head shape, sometimes caused by consistent positioning of the baby on its side. Scaphocephaly, derived from the Greek skaphe, describes the specific variety of a long narrow head that resembles an inverted boat. Like brachycephaly, scaphocephaly is a deformity of proportion. Premature babies are particularly prone to this deformity since their skulls are so fragile, and a side-lying position is often used in the NICU (Neonatal Intensive Care Unit) for easy access to monitors and other equipment. Orthotic management focuses on normalizing the proportion and overall shape of the head.
Infants with a scaphocephalic head shape will often have difficulty lifting their heads against gravity.
Scaphocephaly is a type of cephalic disorder which occurs when there is a premature fusion of the sagittal suture. The sagittal suture joins together the two parietal bones of the skull. Scaphocephaly is the most common of the craniosynostosis conditions and is characterized by a long, narrow head.
Deformational Brachycephaly is present when the entire back of the baby’s head is flat (central flattening) and the head is very wide. The forehead is often bossed or prominent on both sides, and the height of the head is excessively high. In our experience, deformational brachycephaly without asymmetry accounts for about 1 in 10 of the children referred for treatment.
Babies with this problem often have a history of excessive time in carriers, possibly due to gastric reflux or other medical condition or circumstance that does not allow the baby to be placed on the tummy during daytime hours while awake and supervised.

A routine pattern of sleeping on the back can cause brachycephaly in your child. In these scenarios, the head can flatten uniformly which results in a wider and shorter shape.
Asymmetrical brachycephaly is a common type of brachycephaly where the head is excessively wide and asymmetrical. Of the scans sent to Orthomerica for STARband™ fabrication, asymmetrical brachycephaly is second only to deformational Plagiocephaly in incidence. Orthotic management focuses on improving both symmetry and the disproportion of the baby’s head.
Craniosynostosis is a term that refers to the early closing of one or more of the sutures of an infant’s head. The skull is normally composed of bones which are separated by sutures.
When an infant’s brain grows, open sutures allow the skull to expand and develop a relatively normal head shape. If one or more of the sutures has closed prematurely, it can cause the skull to expand in the direction of the open sutures. This can result in an abnormal head shape. In severe cases, this condition can also cause increased pressure on the growing brain.
